Ribitol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name D-Ribitol[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3S,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | |
| Other names (2R,3S,4S)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol (not recommended) Adonit Adonite Adonitol Adonitrol Pentitol 1,2,3,4,5-Pentanepentol 1,2,3,4,5-Pentanol Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference | 1720524 |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.987 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference | 82894 |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C5H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 152.146 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 102 °C (216 °F; 375 K) |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -91.30·10−6 cm3/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Chemical compound
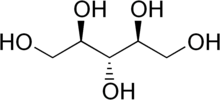
Ribitol, or adonitol, is a crystalline pentose alcohol (C5H12O5) formed by the reduction of ribose. It occurs naturally in the plant Adonis vernalis[2] as well as in the cell walls of some Gram-positive bacteria, in the form of ribitol phosphate, in teichoic acids.[3] It also forms part of the chemical structure of riboflavin and flavin mononucleotide (FMN), which is a nucleotide coenzyme used by many enzymes, the so-called flavoproteins.[4]
References
- ^ "2-Carb-19".
- ^ Advances in Applied Microbiology. Academic Press. 28 October 1997. ISBN 9780080564586.
- ^ Seltmann, Guntram; Holst, Otto (9 March 2013). The Bacterial Cell Wall. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783662048788.
- ^ Mathews, Christopher K. (2000). Biochemistry. Van Holde, K. E. (Kensal Edward), 1928-, Ahern, Kevin G. (3rd ed.). San Francisco, Calif.: Benjamin Cummings. p. 492. ISBN 0805330666. OCLC 42290721.
External links
 Media related to Ribitol at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ribitol at Wikimedia Commons- GMD MS Spectrum
- Safety MSDS data Archived 11 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
- v
- t
- e
Alcohols
| Alcohols found in alcoholic drinks |
|
|---|---|
| Medical alcohol |
|
| Toxic alcohols |
alcohols (1°)
| Methanol | |
|---|---|
| Ethanol |
|
| Butanol |
|
| Straight-chain saturated C1 — C9 |
|
| Straight-chain saturated C10 — C19 |
|
| Straight-chain saturated C20 — C29 |
|
| Straight-chain saturated C30 — C39 |
|
| Straight-chain saturated C40 — C49 |
|
alcohols (2°)
alcohols (3°)
- 2-Methyl-2-pentanol
- 2-Methylheptan-2-ol
- 2-Methylhexan-2-ol
- 3-Methyl-3-pentanol
- 3-Methyloctan-3-ol
- Diacetone alcohol
- Ethchlorvynol
- Methylpentynol
- Nonafluoro-tert-butyl alcohol
- tert-Amyl alcohol
- tert-Butyl alcohol
- Triphenylethanol
- Triphenylmethanol
| Monohydric alcohols |
|
|---|---|
| Dihydric alcohols | |
| Trihydric alcohols | |
| Polyhydric alcohols (sugar alcohols) |
|
fatty alcohols
unsaturated
fatty alcohols
- 3-Methyl-3-pentanol
- Erucyl alcohol
- Linolenyl alcohol
- Linoleyl alcohol
- Oleyl alcohol
- Palmitoleyl alcohol
- tert-Amyl alcohol
- tert-Butyl alcohol
| C1 — C7 |
|
|---|---|
| Deoxy sugar alcohols | |
| Cyclic sugar alcohols | |
| Glycylglycitols |
| Monoterpene alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Sesquiterpene alcohols | |
| Diterpene alcohols |
- 1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol
- 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol
- 2-Fluoroethanol
- Nonafluoro-tert-butyl alcohol
- Trifluoromethanol
 Category
Category
 | This article about an alcohol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e













