Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| RANGAP1 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1Z5S, 2GRN, 2GRO, 2GRP, 2GRQ, 2GRR, 2IY0, 3UIN, 3UIO, 3UIP, 5D2M, 2IO2, 2IO3 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | RANGAP1, Fug1, RANGAP, SD, Ran GTPase activating protein 1 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 602362; MGI: 103071; HomoloGene: 55700; GeneCards: RANGAP1; OMA:RANGAP1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 22 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 22q13.2 | Start | 41,244,779 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 41,286,187 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 15 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 15 E1|15 38.21 cM | Start | 81,588,449 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 81,629,731 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - left testis
- right testis
- Brodmann area 10
- right frontal lobe
- cingulate gyrus
- anterior cingulate cortex
- skin of abdomen
- Brodmann area 9
- skin of leg
- middle frontal gyrus
|
| | Top expressed in | - dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- superior surface of tongue
- spermatid
- yolk sac
- visual cortex
- superior frontal gyrus
- seminiferous tubule
- gallbladder
- primary visual cortex
- epiblast
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 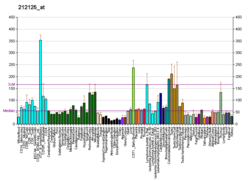
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- cadherin binding
- RNA binding
- GTPase activator activity
- ubiquitin protein ligase binding
| | Cellular component | - intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
- cytoplasmic periphery of the nuclear pore complex
- nuclear pore
- chromosome
- dendrite
- nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments
- mitotic spindle
- chromosome, centromeric region
- cytoskeleton
- nucleus
- kinetochore
- axon cytoplasm
- cytoplasm
- cytosol
- aggresome
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
- nuclear envelope
- nucleoplasm
- spindle
- nuclear membrane
| | Biological process | - cellular response to vasopressin
- protein sumoylation
- cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus
- negative regulation of protein export from nucleus
- response to axon injury
- signal transduction
- sister chromatid cohesion
- activation of GTPase activity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001278651
NM_002883
NM_001317930 |
| |
|---|
NM_001146174
NM_011241
NM_001358622 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001265580
NP_001304859
NP_002874 |
| |
|---|
NP_001139646
NP_035371
NP_001345551 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 22: 41.24 – 41.29 Mb | Chr 15: 81.59 – 81.63 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Ran GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANGAP1 gene.[5][6]
Function
RanGAP1, is a homodimeric 65-kD polypeptide that specifically induces the GTPase activity of RAN, but not of RAS by over 1,000-fold. RanGAP1 is the immediate antagonist of RCC1, a regulator molecule that keeps RAN in the active, GTP-bound state. The RANGAP1 gene encodes a 587-amino acid polypeptide. The sequence is unrelated to that of GTPase activators for other RAS-related proteins, but is 88% identical to Rangap1 (Fug1), the murine homolog of yeast Rna1p. RanGAP1 and RCC1 control RAN-dependent transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm. RanGAP1 is a key regulator of the RAN GTP/GDP cycle.[6]
Interactions
RanGAP1 is a trafficking protein which helps transport other proteins from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Small ubiquitin-related modifier needs to be associated with it before it can be localized at the nuclear pore.[7]
RANGAP1 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000100401 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022391 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Bischoff FR, Krebber H, Kempf T, Hermes I, Ponstingl H (Apr 1995). "Human RanGTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 is a homologue of yeast Rna1p involved in mRNA processing and transport". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 92 (5): 1749–53. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.1749B. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.5.1749. PMC 42597. PMID 7878053.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: RANGAP1 Ran GTPase activating protein 1".
- ^ Hochstrasser M (2000). "Biochemistry. All in the ubiquitin family". Science. 289 (5479): 563–4. doi:10.1126/science.289.5479.563. PMID 10939967. S2CID 32469429.
- ^ Hillig RC, Renault L, Vetter IR, Drell T, Wittinghofer A, Becker J (Jun 1999). "The crystal structure of rna1p: a new fold for a GTPase-activating protein". Mol. Cell. 3 (6): 781–91. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)80010-1. PMID 10394366.
- ^ Becker J, Melchior F, Gerke V, Bischoff FR, Ponstingl H, Wittinghofer A (May 1995). "RNA1 encodes a GTPase-activating protein specific for Gsp1p, the Ran/TC4 homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (20): 11860–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.20.11860. PMID 7744835.
- ^ Bischoff FR, Klebe C, Kretschmer J, Wittinghofer A, Ponstingl H (Mar 1994). "RanGAP1 induces GTPase activity of nuclear Ras-related Ran". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (7): 2587–91. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.2587B. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.7.2587. PMC 43414. PMID 8146159.
- ^ Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- ^ Tatham MH, Kim S, Yu B, Jaffray E, Song J, Zheng J, Rodriguez MS, Hay RT, Chen Y (Aug 2003). "Role of an N-terminal site of Ubc9 in SUMO-1, -2, and -3 binding and conjugation". Biochemistry. 42 (33): 9959–69. doi:10.1021/bi0345283. PMID 12924945.
- ^ Knipscheer P, Flotho A, Klug H, Olsen JV, van Dijk WJ, Fish A, Johnson ES, Mann M, Sixma TK, Pichler A (Aug 2008). "Ubc9 sumoylation regulates SUMO target discrimination". Mol. Cell. 31 (3): 371–82. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.022. PMID 18691969.
Further reading
- Becker J, Melchior F, Gerke V, Bischoff FR, Ponstingl H, Wittinghofer A (1995). "RNA1 encodes a GTPase-activating protein specific for Gsp1p, the Ran/TC4 homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (20): 11860–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.20.11860. PMID 7744835.
- Bischoff FR, Klebe C, Kretschmer J, Wittinghofer A, Ponstingl H (1994). "RanGAP1 induces GTPase activity of nuclear Ras-related Ran". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (7): 2587–91. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.2587B. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.7.2587. PMC 43414. PMID 8146159.
- Krebber H, Ponstingl H (1997). "Ubiquitous expression and testis-specific alternative polyadenylation of mRNA for the human Ran GTPase activator RanGAP1". Gene. 180 (1–2): 7–11. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00389-7. PMID 8973340.
- Matunis MJ, Coutavas E, Blobel G (1997). "A novel ubiquitin-like modification modulates the partitioning of the Ran-GTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 between the cytosol and the nuclear pore complex". J. Cell Biol. 135 (6 Pt 1): 1457–70. doi:10.1083/jcb.135.6.1457. PMC 2133973. PMID 8978815.
- Mahajan R, Delphin C, Guan T, Gerace L, Melchior F (1997). "A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2". Cell. 88 (1): 97–107. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81862-0. PMID 9019411.
- Görlich D, Dabrowski M, Bischoff FR, Kutay U, Bork P, Hartmann E, Prehn S, Izaurralde E (1997). "A Novel Class of RanGTP Binding Proteins". J. Cell Biol. 138 (1): 65–80. doi:10.1083/jcb.138.1.65. PMC 2139951. PMID 9214382.
- Scheffzek K, Ahmadian MR, Kabsch W, Wiesmüller L, Lautwein A, Schmitz F, Wittinghofer A (1998). "The Ras-RasGAP complex: structural basis for GTPase activation and its loss in oncogenic Ras mutants". Science. 277 (5324): 333–8. doi:10.1126/science.277.5324.333. PMID 9219684.
- Mahajan R, Gerace L, Melchior F (1998). "Molecular Characterization of the SUMO-1 Modification of RanGAP1 and Its Role in Nuclear Envelope Association". J. Cell Biol. 140 (2): 259–70. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.2.259. PMC 2132567. PMID 9442102.
- Kamitani T, Kito K, Nguyen HP, Fukuda-Kamitani T, Yeh ET (1998). "Characterization of a second member of the sentrin family of ubiquitin-like proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (18): 11349–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.18.11349. PMID 9556629.
- Okuma T, Honda R, Ichikawa G, Tsumagari N, Yasuda H (1999). "In vitro SUMO-1 modification requires two enzymatic steps, E1 and E2". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 254 (3): 693–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9995. PMID 9920803.
- Hillig RC, Renault L, Vetter IR, Drell T, Wittinghofer A, Becker J (1999). "The crystal structure of rna1p: a new fold for a GTPase-activating protein". Mol. Cell. 3 (6): 781–91. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)80010-1. PMID 10394366.
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, Chissoe S, Hunt AR, Collins JE, Bruskiewich R, Beare DM, Clamp M, Smink LJ, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Babbage A, Bagguley C, Bailey J, Barlow K, Bates KN, Beasley O, Bird CP, Blakey S, Bridgeman AM, Buck D, Burgess J, Burrill WD, O'Brien KP (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–95. Bibcode:1999Natur.402..489D. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Nagase T, Nakayama M, Nakajima D, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 8 (2): 85–95. doi:10.1093/dnares/8.2.85. PMID 11347906.
- Bernier-Villamor V, Sampson DA, Matunis MJ, Lima CD (2002). "Structural basis for E2-mediated SUMO conjugation revealed by a complex between ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 and RanGAP1". Cell. 108 (3): 345–56. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00630-X. PMID 11853669.
- Joseph J, Tan SH, Karpova TS, McNally JG, Dasso M (2002). "SUMO-1 targets RanGAP1 to kinetochores and mitotic spindles". J. Cell Biol. 156 (4): 595–602. doi:10.1083/jcb.200110109. PMC 2174074. PMID 11854305.
- Zhang H, Saitoh H, Matunis MJ (2002). "Enzymes of the SUMO Modification Pathway Localize to Filaments of the Nuclear Pore Complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (18): 6498–508. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.18.6498-6508.2002. PMC 135644. PMID 12192048.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J, Cohn MA, Cantley LC, Gygi SP (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Macauley MS, Errington WJ, Okon M, Schärpf M, Mackereth CD, Schulman BA, McIntosh LP (2005). "Structural and dynamic independence of isopeptide-linked RanGAP1 and SUMO-1". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (47): 49131–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408705200. PMID 15355965.
PDB gallery
-
1z5s: Crystal structure of a complex between UBC9, SUMO-1, RANGAP1 and NUP358/RANBP2 -
2grn: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9 -
2gro: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-N85Q -
2grp: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-Y87A -
2grq: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127A -
2grr: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127S -
2io2: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-1 -
2io3: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-2 -
2iy0: SENP1 (MUTANT) SUMO1 RANGAP |

 1z5s: Crystal structure of a complex between UBC9, SUMO-1, RANGAP1 and NUP358/RANBP2
1z5s: Crystal structure of a complex between UBC9, SUMO-1, RANGAP1 and NUP358/RANBP2 2grn: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9
2grn: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9 2gro: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-N85Q
2gro: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-N85Q 2grp: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-Y87A
2grp: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-Y87A 2grq: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127A
2grq: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127A 2grr: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127S
2grr: Crystal Structure of human RanGAP1-Ubc9-D127S 2io2: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-1
2io2: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-1 2io3: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-2
2io3: Crystal structure of human Senp2 in complex with RanGAP1-SUMO-2 2iy0: SENP1 (MUTANT) SUMO1 RANGAP
2iy0: SENP1 (MUTANT) SUMO1 RANGAP