Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| LHB |
|---|
|
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | LHB, CGB4, LSH-B, hHH23, Luteinizing hormone beta polypeptide, LSH-beta, Luteinizing hormone subunit beta |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 152780; MGI: 96782; HomoloGene: 81806; GeneCards: LHB; OMA:LHB - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 19q13.33 | Start | 49,015,980 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 49,017,091 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - anterior pituitary
- gonad
- testicle
- body of pancreas
- endothelial cell
- left testis
- placenta
- right testis
- stromal cell of endometrium
- body of stomach
|
| | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 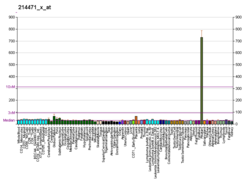 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - signaling receptor binding
- hormone activity
| | Cellular component | - Golgi lumen
- extracellular region
- extracellular space
- cytoplasm
| | Biological process | - cell-cell signaling
- progesterone biosynthetic process
- male gonad development
- peptide hormone processing
- signal transduction
- hormone-mediated signaling pathway
- ovulation
- regulation of signaling receptor activity
- G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 19: 49.02 – 49.02 Mb | n/a |
|---|
| PubMed search | [2] | [3] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Luteinizing hormone subunit beta also known as lutropin subunit beta or LHβ is a polypeptide that in association with an alpha subunit common to all gonadotropin hormones forms the reproductive signaling molecule luteinizing hormone. In humans it is encoded by the LHB gene.[4][5]
Gene
The luteinizing hormone beta subunit is encoded by a single gene in all mammals. In primates, this gene is located within a cluster that arose through gene duplication, and also includes multiple redundant genes encoding the beta subunit of chorionic gonadotropin as well as several nonfunctional pseudogenes. In humans these are contiguous on chromosome 19q13.3.[5] In equids the beta subunit polypeptides of luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin are identical in sequence, differing only in their carbohydrate side-chains, and are the product of a single gene.[6]
Function
This gene is a member of the glycoprotein hormone beta chain family and encodes the beta subunit of luteinizing hormone (LH). Glycoprotein hormones are heterodimers consisting of a common alpha subunit and a unique beta subunit (this protein) which confers biological specificity. LH is expressed in the pituitary gland and promotes spermatogenesis and ovulation by stimulating the testes and ovaries to synthesize steroids.[5]
Clinical significance
Mutations in this gene are associated with hypogonadism which is characterized by infertility and pseudohermaphroditism.[5]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000104826 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Sairam MR, Li CH (Feb 1976). "Human pituitary lutropin. Isolation, properties, and the complete amino acid sequence of the beta-subunit". Biochim Biophys Acta. 412 (1): 70–81. doi:10.1016/0005-2795(75)90340-2. PMID 1191677.
- ^ a b c d "Entrez Gene: LHB luteinizing hormone beta polypeptide".
- ^ Sherman GB, Wolfe MW, Farmerie TA, Clay CM, Threadgill DS, Sharp DC, Nilson JH (June 1992). "A single gene encodes the beta-subunits of equine luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin". Mol. Endocrinol. 6 (6): 951–9. doi:10.1210/mend.6.6.1379674. PMID 1379674.
Further reading
- Keutmann HT, Hua QX, Weiss MA (1992). "Structure of a receptor-binding fragment from human luteinizing hormone beta-subunit determined by [1H]- and [15N]nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy". Mol. Endocrinol. 6 (6): 904–13. doi:10.1210/mend.6.6.1495492. PMID 1495492.
- Weiss J, Axelrod L, Whitcomb RW, et al. (1992). "Hypogonadism caused by a single amino acid substitution in the beta subunit of luteinizing hormone". N. Engl. J. Med. 326 (3): 179–83. doi:10.1056/NEJM199201163260306. PMID 1727547.
- Weisshaar G, Hiyama J, Renwick AG, Nimtz M (1991). "NMR investigations of the N-linked oligosaccharides at individual glycosylation sites of human lutropin". Eur. J. Biochem. 195 (1): 257–68. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15702.x. PMID 1991473.
- Jameson JL, Lindell CM, Habener JF (1986). "Evolution of different transcriptional start sites in the human luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin beta-subunit genes". DNA. 5 (3): 227–34. doi:10.1089/dna.1986.5.227. PMID 2424697.
- Keutmann HT, Charlesworth MC, Mason KA, et al. (1987). "A receptor-binding region in human choriogonadotropin/lutropin beta subunit". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (7): 2038–42. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.2038K. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.7.2038. PMC 304579. PMID 3470775.
- Shome B, Parlow AF (1973). "The primary structure of the hormone-specific, beta subunit of human pituitary luteinizing hormone (hLH)". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 36 (3): 618–21. doi:10.1210/jcem-36-3-618. PMID 4685398.
- Closset J, Hennen G, Lequin RM (1973). "Human luteinizing hormone. The amino acid sequence of the subunit". FEBS Lett. 29 (2): 97–100. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(73)80534-4. PMID 4719207. S2CID 221422600.
- Talmadge K, Vamvakopoulos NC, Fiddes JC (1984). "Evolution of the genes for the beta subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin and luteinizing hormone". Nature. 307 (5946): 37–40. Bibcode:1984Natur.307...37T. doi:10.1038/307037a0. PMID 6690982. S2CID 4282776.
- Beitins IZ, Axelrod L, Ostrea T, et al. (1981). "Hypogonadism in a male with an immunologically active, biologically inactive luteinizing hormone: characterization of the abnormal hormone". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 52 (6): 1143–9. doi:10.1210/jcem-52-6-1143. PMID 6785294.
- Berger P, Kranewitter W, Madersbacher S, et al. (1994). "Eutopic production of human chorionic gonadotropin beta (hCG beta) and luteinizing hormone beta (hLH beta) in the human testis". FEBS Lett. 343 (3): 229–33. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)80561-X. PMID 7513655. S2CID 85383781.
- Keutmann HT, Rubin DA (1993). "A subunit interaction site in human luteinizing hormone: identification by photoaffinity cross-linking". Endocrinology. 132 (3): 1305–12. doi:10.1210/endo.132.3.7679977. PMID 7679977.
- Herrlich A, Kühn B, Grosse R, et al. (1996). "Involvement of Gs and Gi proteins in dual coupling of the luteinizing hormone receptor to adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase C". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (28): 16764–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.28.16764. PMID 8663226.
- Muyan M, Furuhashi M, Sugahara T, Boime I (1997). "The carboxy-terminal region of the beta-subunits of luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin differentially influence secretion and assembly of the heterodimers". Mol. Endocrinol. 10 (12): 1678–87. doi:10.1210/mend.10.12.8961276. PMID 8961276.
- Roy AC, Liao WX, Chen Y, et al. (1997). "Identification of seven novel mutations in LH beta-subunit gene by SSCP". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 165 (2): 151–3. doi:10.1007/bf00229477. PMID 8979264. S2CID 37938552.
- Liao WX, Roy AC, Chan C, et al. (1998). "A new molecular variant of luteinizing hormone associated with female infertility". Fertil. Steril. 69 (1): 102–6. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(97)00445-7. PMID 9457942.
- O'Connor JF, Kovalevskaya G, Birken S, et al. (1998). "The expression of the urinary forms of human luteinizing hormone beta fragment in various populations as assessed by a specific immunoradiometric assay". Hum. Reprod. 13 (4): 826–35. doi:10.1093/humrep/13.4.826. PMID 9619532.
- Takahashi K, Kurioka H, Ozaki T, et al. (1999). "Increased prevalence of luteinizing hormone beta-subunit variant in Japanese infertility patients". Hum. Reprod. 13 (12): 3338–44. doi:10.1093/humrep/13.12.3338. PMID 9886510.
- Elter K, Erel CT, Cine N, et al. (1999). "Role of the mutations Trp8 => Arg and Ile15 => Thr of the human luteinizing hormone beta-subunit in women with polycystic ovary syndrome". Fertil. Steril. 71 (3): 425–30. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(98)00491-9. PMID 10065776.
- Jiang M, Pakarinen P, Zhang FP, et al. (1999). "A common polymorphic allele of the human luteinizing hormone beta-subunit gene: additional mutations and differential function of the promoter sequence". Hum. Mol. Genet. 8 (11): 2037–46. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.11.2037. PMID 10484773.
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 19 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

















