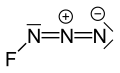Fluorine azide
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names triazadienyl fluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
| ||
InChI
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | FN3 | ||
| Molar mass | 61.019 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Yellow-green gas | ||
| Melting point | −139 °C (−218 °F; 134 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −30 °C (−22 °F; 243 K) | ||
| Explosive data | |||
| Shock sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Friction sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards | Extremely sensitive explosive | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | [citation needed]  0 4 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations | Hydrazoic acid Chlorine azide Bromine azide Iodine azide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Fluorine azide or triazadienyl fluoride is a yellow green gas composed of nitrogen and fluorine with formula FN3.[1] Its properties resemble those of ClN3, BrN3, and IN3.[2] The bond between the fluorine atom and the nitrogen is very weak, leading to this substance being very unstable and prone to explosion.[3] Calculations show the F–N–N angle to be around 102° with a straight line of 3 nitrogen atoms.[4]
The gas boils at –30° and melts at –139 °C.[5]
It was first made by John F. Haller in 1942.[6]
Reactions
Fluorine azide can be made by reacting hydrazoic acid or sodium azide, with fluorine gas.[5][7]
- HN3 + F2 → N3F + HF
- NaN3 + F2 → N3F + NaF
Fluorine azide decomposes without explosion at normal temperatures to make dinitrogen difluoride:
- 2 FN3 → N2F2 + 2 N2.[1]
At higher temperatures such as 1000 °C fluorine azide breaks up into nitrogen monofluoride radical:[7]
- FN3 → NF + N2
The FN itself dimerizes on cooling.
- 2 NF → N2F2
Solid or liquid FN3 can explode, releasing a large amount of energy. A thin film burns at the rate of 1.6 km/s.[8] Due to the explosion hazard, only very small quantities of this substance should be handled at a time.[9]
FN3 adducts can be formed with the Lewis acids boron trifluoride (BF3) and arsenic pentafluoride (AsF5) at -196 °C. These molecules bond with the Nα atom.[10]
Properties
Spectroscopy
| Parameter | Value[9] | Unit |
| A | 48131.448 | MHz |
| B | 5713.266 | MHz |
| C | 5095.276 | MHz |
| μa | 1.1 | |
| μb | 0.7 |
Shape
Distances between atoms are F–N 0.1444 nm, FN=NN 0.1253 nm and FNN=N 0.1132 nm.[9]
Physical
FN3 has a density of 1.3 g/cm3.[11]
FN3 adsorbs on to solid surfaces of potassium fluoride, but not onto lithium fluoride or sodium fluoride. This property was being investigated so that FN3 could boost the energy of solid propellants.[11]
The ultraviolet photoelectric spectrum shows ionisation peaks at 11.01, 13,72, 15.6, 15.9, 16.67, 18.2, and 19.7 eV. Respectively these are assigned to the orbitals: π, nN or nF, nF, πF, nN or σ, π and σ.[3]
References
- ^ a b Gipstein, Edward; John F. Haller (1966). "Absorption Spectrum of Fluorine Azide". Applied Spectroscopy. 20 (6): 417–418. Bibcode:1966ApSpe..20..417G. doi:10.1366/000370266774386470. ISSN 0003-7028. S2CID 96337253.
- ^ Saxena, P. B. (2007-01-01). Chemistry of Interhalogen Compounds. Discovery Publishing House. p. 96. ISBN 9788183562430. Retrieved 16 June 2014.
- ^ a b Rademacher, Paul; Andreas J. Bittner; Gabriele Schatte; Helge Willner (1988). "Photoelectron Spectrum and Electronic Structure of Triazadienyl Fluoride, N3F". Chemische Berichte. 121 (3): 555–557. doi:10.1002/cber.19881210325. ISSN 0009-2940.
- ^ Peters, Nancy J. S.; Leland C. Allen; Raymond A. Firestone (1988). "Fluorine azide and fluorine nitrate: structure and bonding". Inorganic Chemistry. 27 (4): 755–758. doi:10.1021/ic00277a035. ISSN 0020-1669.
- ^ a b Gholivand, Khodayar; Gabriele Schatte; Helge Willner (1987). "Properties of triazadienyl fluoride, N3F". Inorganic Chemistry. 26 (13): 2137–2140. doi:10.1021/ic00260a025. ISSN 0020-1669.
- ^ Lowe, Derek (21 October 2008). "Things I Won't Work With: Triazadienyl Fluoride". In the Pipeline. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ^ a b Benard, D. J.; B. K. Winker; T. A. Seder; R. H. Cohn (1989). "Production of nitrogen monofluoride (a1Δ) by dissociation of fluorine azide". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 93 (12): 4790–4796. doi:10.1021/j100349a022. ISSN 0022-3654.
- ^ Seder, T.A.; D.J. Benard (1991). "The decomposition of condensed phase fluorine azide". Combustion and Flame. 85 (3–4): 353–362. doi:10.1016/0010-2180(91)90139-3. ISSN 0010-2180.
- ^ a b c Christen, Dines.; H. G. Mack; G. Schatte; H. Willner (1988). "Structure of triazadienyl fluoride, FN3, by microwave, infrared, and ab initio methods". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 110 (3): 707–712. doi:10.1021/ja00211a007. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Schatte, G.; H. Willner (1991). "Die Wechselwirkung von N3F mit Lewis-Säuren und HF. N3F als möglicher Vorläufer für die Synthese von N3+-Salzen = The interaction of N3F with Lewis acids and HF•N3F as possible precursor for the synthesis of N3+ salts". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B (in German). 46 (4): 483–489. doi:10.1515/znb-1991-0410. ISSN 0932-0776. S2CID 97045269.
- ^ a b Brener, Nathan E.; Kestner, Neil R.; Callaway, Joseph (December 1990). Theoretical Studies of Highly Energetic CBES Materials: Final Report for the Period 2 March 1987 to 31 May 1987 (PDF). Louisiana State University, Department of Physics and Astronomy. pp. 21–27. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
External links
 Media related to Fluorine azide at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fluorine azide at Wikimedia Commons
- v
- t
- e
| HF | He | |||||||||||||||||
| LiF | BeF2 | BF BF3 B2F4 | CF4 CxFy | NF3 N2F4 | OF OF2 O2F2 O2F | F− | Ne | |||||||||||
| NaF | MgF2 | AlF AlF3 | SiF4 | P2F4 PF3 PF5 | S2F2 SF2 S2F4 SF4 S2F10 SF6 | ClF ClF3 ClF5 | HArF ArF2 | |||||||||||
| KF | CaF2 | ScF3 | TiF3 TiF4 | VF2 VF3 VF4 VF5 | CrF2 CrF3 CrF4 CrF5 CrF6 | MnF2 MnF3 MnF4 | FeF2 FeF3 | CoF2 CoF3 | NiF2 NiF3 | CuF CuF2 | ZnF2 | GaF3 | GeF4 | AsF3 AsF5 | SeF4 SeF6 | BrF BrF3 BrF5 | KrF2 KrF4 KrF6 | |
| RbF | SrF2 | YF3 | ZrF4 | NbF4 NbF5 | MoF4 MoF5 MoF6 | TcF6 | RuF3 RuF4 RuF5 RuF6 | RhF3 RhF5 RhF6 | PdF2 Pd[PdF6] PdF4 PdF6 | AgF AgF2 AgF3 Ag2F | CdF2 | InF3 | SnF2 SnF4 | SbF3 SbF5 | TeF4 TeF6 | IF IF3 IF5 IF7 | XeF2 XeF4 XeF6 XeF8 | |
| CsF | BaF2 | * | LuF3 | HfF4 | TaF5 | WF4 WF6 | ReF6 ReF7 | OsF4 OsF5 OsF6 OsF 7 OsF8 | IrF3 IrF5 IrF6 | PtF2 Pt[PtF6] PtF4 PtF5 PtF6 | AuF AuF3 Au2F10 AuF5·F2 | HgF2 Hg2F2 HgF4 | TlF TlF3 | PbF2 PbF4 | BiF3 BiF5 | PoF4 PoF6 | At | RnF2 RnF6 |
| Fr | RaF2 | ** | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| ↓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| * | LaF3 | CeF3 CeF4 | PrF3 PrF4 | NdF3 | PmF3 | SmF2 SmF3 | EuF2 EuF3 | GdF3 | TbF3 TbF4 | DyF3 | HoF3 | ErF3 | TmF2 TmF3 | YbF2 YbF3 | ||||
| ** | AcF3 | ThF4 | PaF4 PaF5 | UF3 UF4 UF5 UF6 | NpF3 NpF4 NpF5 NpF6 | PuF3 PuF4 PuF5 PuF6 | AmF3 AmF4 AmF6 | CmF3 | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | ||||
- AgPF6
- KAsF6
- LiAsF6
- NaAsF6
- HPF6
- HSbF6
- NH4PF6
- KPF6
- KSbF6
- LiPF6
- NaPF6
- NaSbF6
- TlPF6
- Cs2AlF5
- K3AlF6
- Na3AlF6
and pseudohalogenides
- BaSiF6
- BaGeF6
- (NH4)2SiF6
- Na2[SiF6]
- K2[SiF6]
- CBrF3
- CBr2F2
- CBr3F
- CClF3
- CCl2F2
- CCl3F
- CF2O
- CF3I
- CHF3
- CH2F2
- CH3F
- C2Cl3F3
- C2H3F
- C6H5F
- C7H5F3
- C15F33N
- C3H5F
- C6H11F
lanthanide, actinide, ammonium
- VOF3
- CrOF4
- CrF2O2
- NH4F
- (NH4)2ZrF6
- CsXeF7
- Li2TiF6
- Li2ZrF6
- K2TiF6
- Rb2TiF6
- Na2TiF6
- Na2ZrF6
- K2NbF7
- K2TaF7
- K2ZrF6
- UO2F2
- FNO
- FNO2
- FNO3
- KHF2
- NaHF2
- NH4HF2
and iodosyl
- F2OS
- F3OP
- PSF3
- IOF3
- IO3F
- IOF5
- IO2F
- IO2F3