Andrew Loomis
Andrew Loomis | |
|---|---|
| Born | William Andrew Loomis (1892-06-15)June 15, 1892 Syracuse, New York, U.S. |
| Died | May 25, 1959(1959-05-25) (aged 66) |
| Nationality | American |
| Education | Art Students League of New York Art Institute of Chicago |
| Known for | Painting, illustrator, author |
| Notable work | Figure Drawing for All It's Worth Fun With a Pencil |
William Andrew Loomis (June 15, 1892 – May 25, 1959) was an American illustrator, writer, and art instructor. His commercial work was featured prominently in advertising and magazines. However, Loomis is best known as the writer of a series of instructional art books printed throughout the 20th century, and also as the inventor of the "Loomis method". Long after his death, Loomis's realistic style has continued to influence popular artists.
Early life
Loomis was born on June 15, 1892, in Syracuse, New York. Loomis grew up in Zanesville, Ohio, and spent much of his working life in Chicago, Illinois. He studied at the Art Students League of New York under George Bridgman and Frank DuMond when he was 19.[1] Loomis then went back to Chicago to work at an art studio[1] and study at the Art Institute of Chicago.[2]
Career


After military service in World War I, Loomis worked for a couple of advertising agencies before opening his own studio in downtown Chicago in 1922.[3] From that time until the late 1930s Loomis produced advertising paintings for many large companies such as Coca-Cola, Studebaker, Palmolive, Quaker Oats, Munsingwear,[3] and Kellogg's.[4] He was the official portrait painter of the Dionne quintuplets,[3] and he created Jack and Bingo for the cover of the Cracker Jack box. In 1932, Loomis created paintings for the advertisements that would introduce 3 Musketeers. One of those paintings was a portrait of a Mars chemist, Frances Herdlinger. Herdlinger was one of three women chemists working regularly with Forrest Mars Sr. on the development of the new candy bar.[5][6]
In the 1930s, he taught at the American Academy of Art. It was during this time that his teaching techniques were compiled for his first book, Fun With a Pencil (1939).[7]
Loomis would go on to release several more books in the coming decades, including one of his most popular, Figure Drawing for All It's Worth (1943).[8] Many of the books exhibit his own personally crafted techniques – such as the "ball and plane" method of head drawing – guided by Loomis's humorous dialogue. Many of the titles gained strong appeal for their academic value and went through several printings during the 20th century. Loomis died in 1959, but his final book, The Eye of the Painter and the Elements of Beauty (1961), was printed posthumously.[9]
The Loomis method
The Loomis Method is a drawing technique that uses grids to represent the human head from various angles accurately. This technique was developed by Loomis in the 1940s, and was first described in his book Drawing the Head from Hands.[10] The Loomis method for the construction of the head is very popular because it is easy to learn and remember and can be applied to any drawing of the head.[11]
Influence and legacy
Titan Books reissued the Andrew Loomis titles in facsimile editions between 2011 and 2013. Prior to that, the books had been out of print for decades, available only as excerpts by Walter Foster Publishing. Some of Loomis's books are currently being published in Japanese via Maar Sha Co., Ltd. Early prints have become highly collectible, sought by art enthusiasts and practitioners.
-
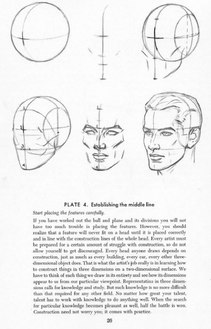 From Drawing the Head and Hands
From Drawing the Head and Hands -
 From Drawing the Head and Hands
From Drawing the Head and Hands -
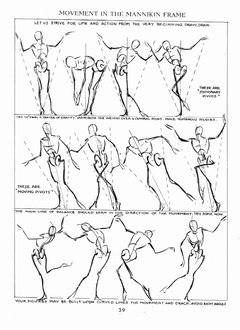 From Figure Drawing for All It's Worth
From Figure Drawing for All It's Worth -
 From Creative Illustration
From Creative Illustration -
 From Successful Drawing
From Successful Drawing
Bibliography
- Fun With a Pencil (1939). Reissued as a full facsimile of the original on April 5, 2013, from Titan Books.
- Figure Drawing for All It's Worth (1943). Reissued as a full facsimile of the original on May 27, 2011, from Titan Books.
- Creative Illustration (1947). Reissued as a full facsimile of the original on October 12, 2012, from Titan Books.
- Successful Drawing (1951). Republished in a revised edition as Three Dimensional Drawing (16 new pages with technical material on perspective replacing the pictorial gallery sections) and reissued as a full facsimile of the original on May 4, 2012, from Titan Books.
- Drawing the Head and Hands (1956). Reissued as a full facsimile of the original on October 21, 2011, from Titan Books.
- The Eye of the Painter and the Elements of Beauty (1961).
- I'd Love to Draw! (2014). Published posthumously by Titan Books, with some of the text written by Alex Ross.
References
- ^ a b Cabrera, Armand (August 1, 2010). "William Andrew Loomis". Art and Influence. Archived from the original on July 28, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2018.
- ^ Cabrera, Armand (August 15, 2010). "Andrew Loomis Quotes on Color". Art and Influence. Archived from the original on July 28, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2018.
- ^ a b c Harris Jr., Jack (2000). Andrew Loomis: A Legacy in Words and Pictures (masters). Syracuse.
- ^ "Andrew Loomis". Norman Rockwell Museum. Archived from the original on September 12, 2017. Retrieved June 30, 2018.
- ^ Carlile, Olga Gize (June 10, 1995). "Three Musketeers Was Her Project". Freeport, IL: Journal Standard.
- ^ Williams, Melissa (May 30, 2018). "Meet Frances Herdlinger". COMO Magazine. Archived from the original on June 29, 2020. Retrieved June 30, 2018.
- ^ Loomis, Andrew (1939). Fun With a Pencil. Viking Press.
- ^ Loomis, Andrew (1943). Figure Drawing for All It's Worth. World Publishing Company.
- ^ Loomis, Andrew (1961). The Eye of the Painter and the Elements of Beauty. Sir Isaac Pitman & Sons.
- ^ "Loomis Method - Beginner's Guide on How To Draw Heads". December 13, 2022. Retrieved March 27, 2024.
- ^ "The Loomis Method of Drawing the Head, a Step-by-Step Guide – GVAAT'S WORKSHOP". gvaat.com. Retrieved March 27, 2024.
External links
- Biography
- Works by or about Andrew Loomis at Internet Archive
- v
- t
- e
1958–1959 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
1960–1969 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
1970–1979 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
1980–1989 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
1990–1999 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
2000–2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
2010–2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
2020–2029 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||















